Langmuir-Hinshelwood Kinetics: ConcepTest and Example Problem
Try to answer this ConcepTest and solve the example problem before using this module. Studies show that trying to answer the questions before studying material improves learning and retention. We suggest that you write down the reasons for your answers. By the end of this module, you should be able to answer these on your own. Answers will be given at the end of this module.

Example Problem 1
The irreversible, gas-phase reaction 2A → B + C is conducted over a solid catalyst. The reaction may be considered isothermal. The following reaction mechanism is proposed, where S represents a surface site.
- A + S ↔ A-S
- A-S + A-S → B-S + C + S
- B-S ↔ B + S
It is proposed that step 2 is rate-determining and irreversible, whereas steps 1 and 3 are equillibrated.
a. Based on the propsed mechanism, derive the Langmuir-Hinshelwood rate expression for the reaction.
b. Experiments with a differential reactor have been used to measure the rate of reaction. The results are shown below. Are the data consistent with the proposed mechanism? Under the experimental conditions, do you expect that the surface mainly consists of vacant sites, sites with adsorbed A, sites with adsorbed B, or sites with adsorbed C? Justify your answers.
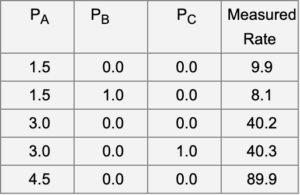
Note: Pressures are in MPa, measured rate is in arbitrary units.
