Liquefaction: Screencast
Describes the Linde liquefaction cycle for converting a room-temperature gas into a low-temperature liquid.
We suggest you list the important points in this screencast as a way to increase retention.
Shows the Linde liquefaction cycle on pressure-enthalpy and temperature-entropy diagrams.
We suggest you list the important points in this screencast as a way to increase retention.
Important Equations:
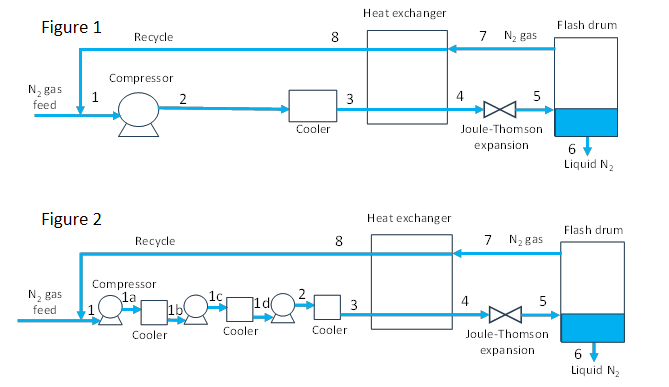
Compressor in Figure 1
\[T_2 \,>\, T_1\]
\[S_2 \,=\, S_1\]
\[W \,=\, H_2 \,-\, H_1\]
Cooler in Figure 1
\(H\) = enthalpy per kg
\(S\) = entropy per kg
\(T\) = temperature
\(W\) = work per kg
\(\dot{Q}\) = rate of heat transfer (kJ/s)
\(\dot{m}_1\) = mass flow rate entering the first compressor (kg/s)
Compressors in Figure 2
\[T_{1a} > T_1\]
\[S_{1a} = S_1\]
\[W_1 = H_{1a}\, -\, H_1\]
\[T_{1c} > T_{1b}\]
\[S_{1c} = S_{1b}\]
\[W_2 = H_{1c} \,-\, H_{1b}\]
\[T_2 > T_{1d}\]
\[S_2 = S_{1d}\]
\[W_3 = H_2 \,-\, H_{1d}\]
Coolers in Figure 2
\[\dot{m}_1(H_{1b} \,-\, H_{1a}) = \dot{Q}_1\]
\[\dot{m}_1(H_{1d} \,-\, H_{1c}) = \dot{Q}_2\]
\[\dot{m}_1(H_3 \,-\, H_2) = \dot{Q}_3\]
Heat exchanger (Figures 1 and 2)
\[\dot{m}_3(H_4 \,-\, H_3) \,+\, \dot{m}_8(H_3 \,-\, H_2) = 0\]
\[(H_4 \,-\, H_3) \,+\, (1\,-\, y)(H_8 \,-\, H_7) = 0\]
where \(y\) = fraction of flow exiting the Joule-Thomson expansion that is liquid
Joule-Thomson expansion (Figures 1 and 2)
\[H_4 = H_3\]
Flash Drum (Figures 1 and 2)
\[H_5 = y\,H_6 \,+\, (1\,-\,y)H_7\]



