Fugacity from Equation of State for Water

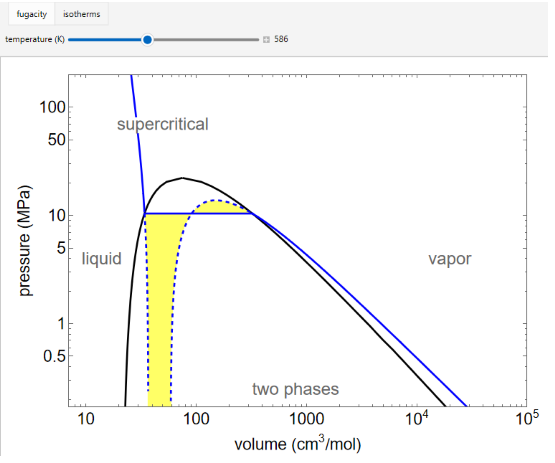
The fugacity f and the fugacity coefficient φ are calculated for water by using the Peng–Robinson equation of state. “Pressure” and “volume” are changed with sliders, and the corresponding state is indicated by the black point on the log pressure versus log volume diagram. The fugacity coefficient indicates how much the fluid deviates from ideal-gas behavior (φ = 1 for an ideal gas). Selecting “isotherms” displays isotherms on the P-V diagram, and the horizontal solid green line represents liquid and vapor in equilibrium. The areas under the curve, which are colored light blue, are equal when viewed on a linear scale.
This simulation runs on desktop using the free Wolfram Player. Download the Wolfram Player here.
About:
This simulation was made at the University of Colorado Boulder, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. Author: Rachael L. Baumann
View the source code for this simulation



