Heats of Reaction: Example Problems
Try to solve these problems before watching the solutions in the screencasts.
Example Problem 1
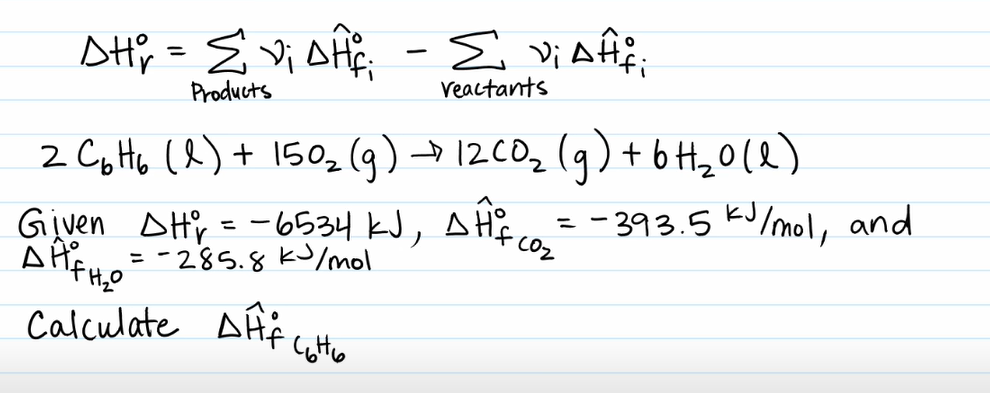
Example Problem 3
Calculate the heat of reaction at 600 K when hydrazine (NH4) decomposes to form nitrogen and hydrogen. The constants for heat capacities, where CP is in J/(mol K) and T is in K, are in the table below.
\[C_{P,i} = A_i + B_iT + C_iT^2 + D_iT^3\]
| gas | \(A_i\) | \(B_i\) |
\(C_i\) |
\(D_i\) |
| NH4 | 16.276 | 1.46E-01 | -9.64E-05 | 2.51E-08 |
| N2 | 28.883 | -1.57E-03 | 8.08E-06 | -2.87E-09 |
| H2 | 29.088 | -1.92E-03 | 4.00E-06 | -8.7E-10 |
Example Problem 2
Determine the enthalpy change of this reaction using heats of formation and material balances. CO(g) + H2O(g) → CO2(g) + H2(g)
The reactants come in at 300°C and the products leave at 500°C. The heats of formation for CO, H2O, and CO2 are -110.53 kJ/mol, -241.83 kJ/mol, and -393.5 kJ/mol, respectively.



