Heterogeneous Chemical Equilibrium: ConcepTest and Example Problem
Try to answer this ConcepTest and solve the example problem before using this module. Studies show that trying to answer the questions before studying material improves learning and retention. We suggest that you write down the reasons for your answers. By the end of this module, you should be able to answer these on your own. Answers will be given at the end of this module.
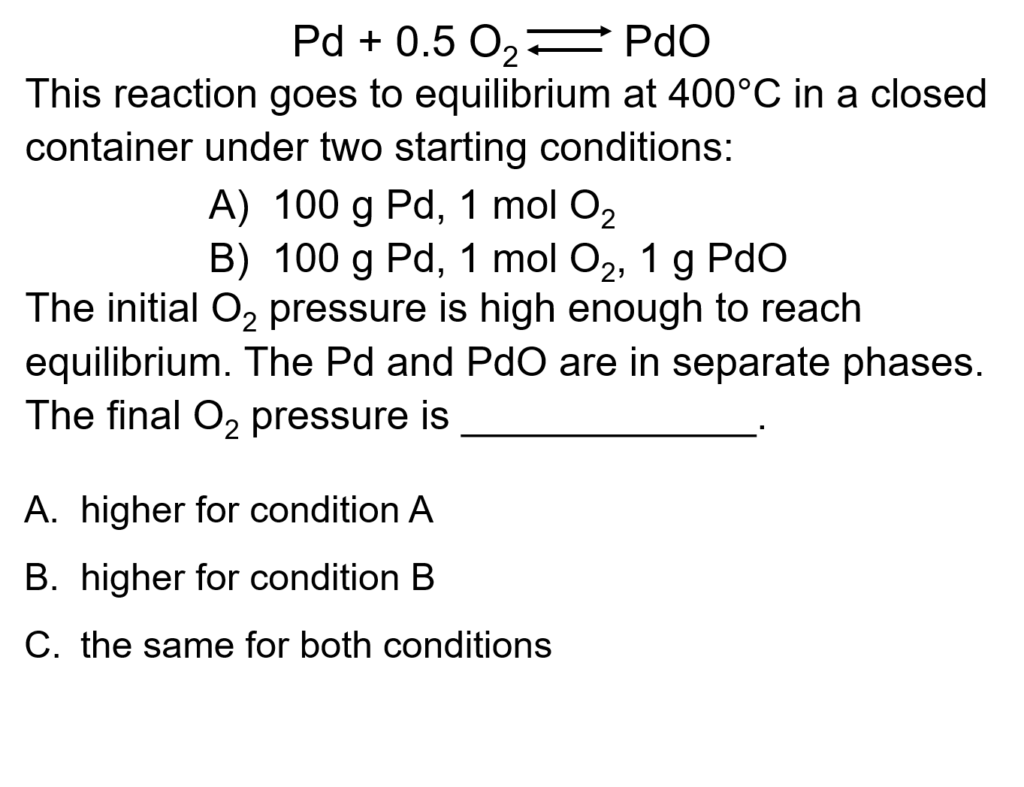
Example Problem 1
Given the Gibbs free energy at two temperatures, determine the maximum temperature for a heterogeneous reaction to occur. For the reaction,
2Ca(liq) + ThO2(crystal) ↔ 2CaO(crystal) + Th(crystal),
∆G° = -3.4 kcal/mol at 1000°C, and
∆G° = -2.0 kcal/mol at 1200°C.
Assume all phases are pure.
