Mass Balance in the Haber Process

Description
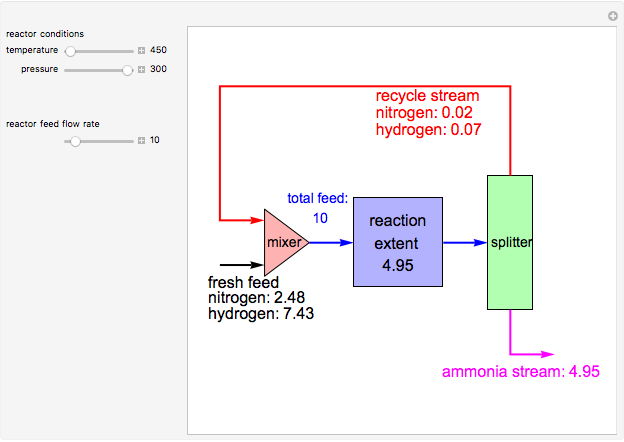
The Haber process is the high-pressure synthesis of ammonia (1.5 H2 + 0.5 N2 ↔ NH3). The Peng-Robinson equation of state and the reaction-coordinate method are used to compute the extent of reaction, ξ in moles of NH3 per unit time, for user-set values of the reactor temperature T (K) and pressure P (bar). This simulation carries out the mass balance around the reactor and splitter in order to compute the amount of ammonia produced when chemical equilibrium is reached in the reactor and in the recycle stream. The splitter separates NH3 perfectly from the reactants (N2, H2), and the fresh feed contains stoichiometric amounts of N2 and H2. As expected from Le Chatelier’s principle, the amount of ammonia produced is greater at low temperatures and high pressures.
About
Authors: Housam Binous, Ahmed Bellagi. Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA.
View the source code for this simulatio



